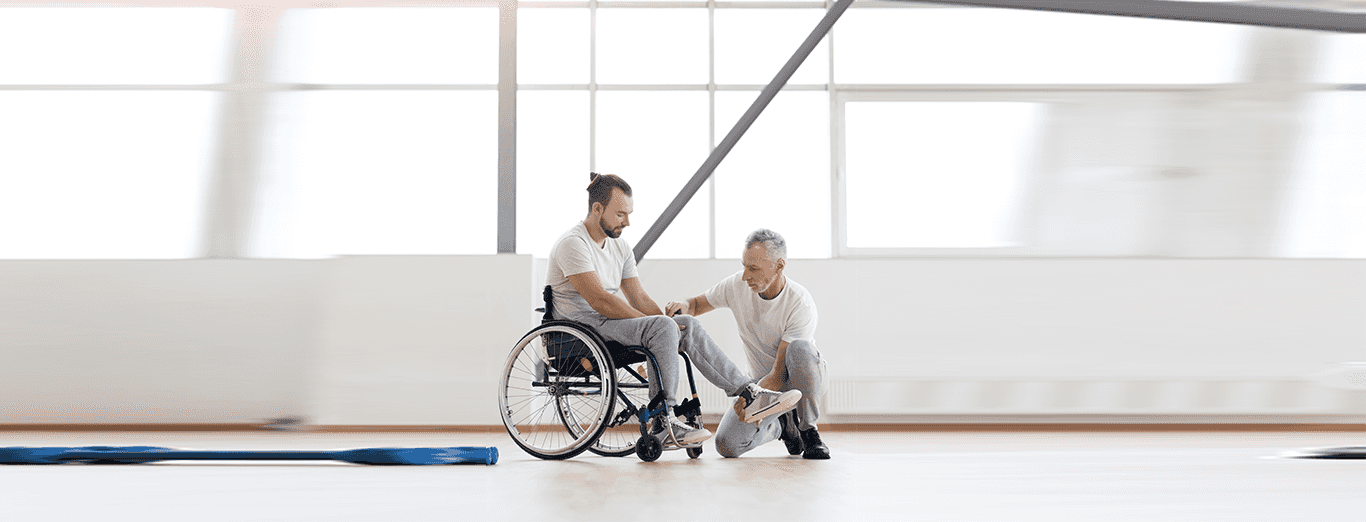
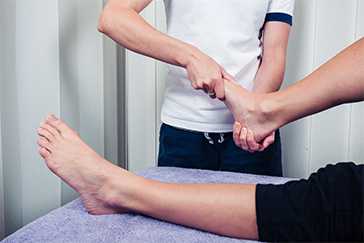
Expert Physiotherapy at Home
Certified physiotherapists visit you at home to provide focused, one-on-one care tailored to your needs. With no travel or waiting rooms, recovery happens in a setting that is comfortable, familiar, and built around your convenience.
Personalised Recovery Programmes
Every treatment plan is designed to suit your condition, goals, and pace. Our physiotherapists follow structured, evolving protocols to ensure consistent progress, with each session aligned to deliver meaningful results.
Trusted Physiotherapists. Real Results.
Our team comprises experienced, background-verified physiotherapists trusted by thousands of families. With a strong focus on safety, reliability, and clinical outcomes, we make recovery at home both effective and reassuring
Patient Testimonials
Portea Physiotherapists for Home Visits
Meet some of our experienced and dedicated healthcare professionals

Dr. Lokesh G
Physiotherapist
Specializations
Experienced in Neurological rehabilitation, Orthopaedic physiotherapy, and Paediatric care
Delivers structured, high-impact treatment plans across neuro, ortho, and paediatrics—ensuring safety, comfort, and measurable recovery at every stage.

Dr. Mohammed Sarwar
Physiotherapist
Specializations
Experienced in Neurological rehabilitation, Adult physiotherapy, and Paediatric care
Combines deep clinical expertise with a compassionate approach, supporting both adults and children through neuro and physical rehabilitation that promotes long-term independence and recovery.

Dr. Nelapati Divya
Physiotherapist
Specializations
Skilled in Orthopaedic rehabilitation, Manual therapy techniques, and Paediatric physiotherapy
Brings a personalised, hands-on approach to healing—combining structural expertise with paediatric sensitivity to restore movement, relieve pain, and improve everyday function.

Dr. Naveen V
Physiotherapist
Specializations
Trained in Pain management, Cardiac and Orthopaedic rehabilitation, Neurological care, and Neural tissue mobilisation
Brings clinical precision and empathy together—designing science-backed recovery protocols for pain relief, nerve mobilisation, and cardio-neuro-ortho rehabilitation across all age groups

Dr. Miloni Savla
Physiotherapist
Specializations
Holds an MPT in Orthopaedics with a focus on Musculoskeletal rehabilitation and strength recovery
Delivers focused, movement-oriented therapy grounded in orthopaedic science—helping patients rebuild strength, restore function, and return to daily life with confidence
Other Cities
Physiotherapy Treatments

types of paralysis
Here are the definitions of different types of paralysis:
Monoplegia: Paralysis that affects a single limb, either an arm or a leg, often caused by conditions such as stroke, trauma, or neurological disorders.
Hemiplegia: Paralysis on one side of the body, either the left or the right, typically resulting from a stroke or brain injury that impacts one hemisphere of the brain.
Paraplegia: Paralysis of the lower half of the body, including both legs and occasionally part of the trunk. It is commonly caused by spinal cord injuries or neurological conditions affecting the lower spinal cord.
Quadriplegia: Paralysis of all four limbs—both arms and legs—usually caused by spinal cord injuries or conditions affecting the cervical spine, leading to loss of function in all limbs.
causes of paralysis and need for physiotherapy
The most common cause of paralysis is a stroke, which can damage the brain and disrupt its connection to the spinal cord.
Here are the primary causes of paralysis:
- Spinal Cord Injury
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Cerebral Palsy
- Post-Polio Syndrome
- Neurofibromatosis
- Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI)
- Birth Defects
These Might be of Interest
symptoms of paralysis and physiotherapy assessment
Our ability to move is governed by the coordination between sensory nerves and the central nervous system. Any disruption in the transmission of nerve signals along the pathway from the brain to the muscles can hinder muscle control.
Common symptoms include:
- Loss of consciousness
- Clumsiness and numbness
- Severe headache
- Difficulty breathing
- Drooling
- Cognitive difficulties, difficulty writing or speaking
- Changes in mood or behavior
- Loss of bladder or bowel control
- Loss or changes in vision and/or hearing
- Nausea with or without vomiting
physiotherapy-based management & treatment options for paralysis
Managing and treating paralysis involves a holistic approach focused on enhancing function, mobility, and overall quality of life. Key strategies include:
- Physical Therapy
- Occupational Therapy
- Medications
- Assistive Devices
- Surgical Interventions
physiotherapy for paralysis: at-home care with portea
Physiotherapy for paralysis is customized to each individual’s condition, based on a thorough neurological assessment. Treatment may include:
- Muscle strengthening exercises
- Joint mobility stretches
- Core stability training
- Dynamic balance exercises
- Gait re-education
- Sensory stimulation
- Functional electrical stimulation
- Hydrotherapy and gym-based rehab
Educating caregivers and providing walking aids or other supportive equipment are also essential.
prevention tips for paralysis and physiotherapy benefits
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle
- Prevent injuries (e.g., wear seatbelts, use helmets)
- Manage chronic conditions (e.g., diabetes, hypertension)
- Get regular check-ups
- Stay updated on vaccinations
- Prevent infections
- Manage stress
- Seek prompt treatment for symptoms
- Maintain a healthy weight
how portea can help you recover with physiotherapy support
At Portea, we bring expert care to the comfort of your home. Our services include:
- Personalized physiotherapy for paralysis
- Targeted pain management
- Customized exercise programs
- Preventive health strategies
- Convenient diagnostics at home
why choose portea for paralysis physiotherapy at home?
With Portea, you’re not just getting treatment; you’re gaining a healthcare partner. We offer:
- Physiotherapists with years of hands-on experience
- Personalized care plans
- Affordable, in-home service
- A dedicated support system for patients and caregivers
other healthcare services by portea
Beyond paralysis care, Portea provides a range of services:
frequently asked questions (faqs)
1. What is physiotherapy treatment for paralysis at home?
Physiotherapy for paralysis at home involves personalized rehabilitation delivered by certified physiotherapists. Treatment may include muscle strengthening exercises, joint mobility stretches, balance training, and functional electrical stimulation, all tailored to your specific condition and recovery goals.
2. How can physiotherapy help in paralysis recovery?
Physiotherapy aids in paralysis recovery by enhancing muscle strength, improving joint flexibility, and promoting neural re-education. Techniques like passive and active-assisted range-of-motion exercises, electrical stimulation, and gait training help restore function and independence.
3. Is home-based physiotherapy effective for paralysis patients?
Yes, home-based physiotherapy offers several advantages, including personalized care, convenience, and a comfortable environment. It allows for consistent therapy sessions, better adherence to treatment plans, and active involvement of family members in the rehabilitation process.
4. How do I book physiotherapy treatment for paralysis at home?
Booking physiotherapy treatment for paralysis at home is straightforward. You can contact reputable providers like Portea Care, who offer certified physiotherapists for home visits. Simply visit their website or call their helpline to schedule an appointment.
5. What types of paralysis can be treated with home physiotherapy?
Home physiotherapy can assist in the rehabilitation of various types of paralysis, including monoplegia (affecting one limb), hemiplegia (one side of the body), paraplegia (both legs), and quadriplegia (all limbs). Treatment plans are customized based on the specific needs of the patient.
6. What should I expect during a home physiotherapy session for paralysis?
During a home physiotherapy session, a certified physiotherapist will assess your condition and design a personalized treatment plan. Sessions may include exercises to improve strength, flexibility, and coordination, as well as techniques to manage pain and prevent complications.
References
Doctor Consultation
Nursing
Physiotherapy
Trained Attendant
Elder Care
Mother & Baby Care
Lab Tests
Medical Equipment
Speciality Pharma
Critical Care