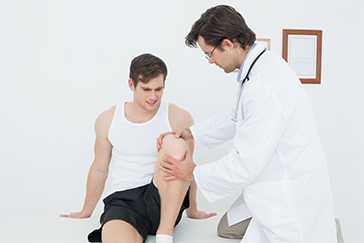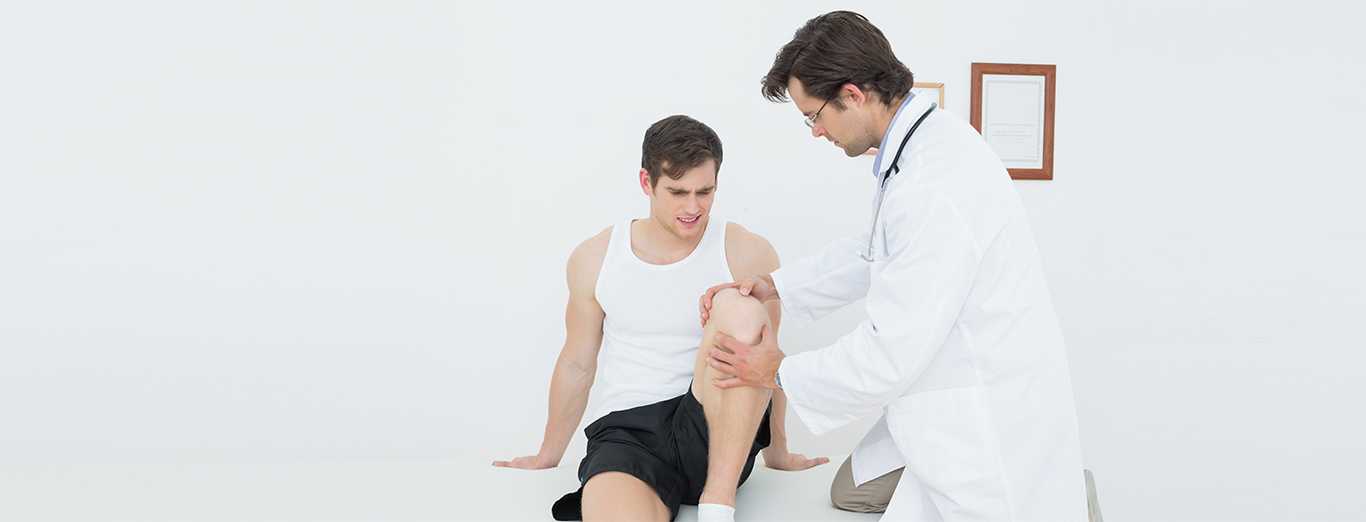
Expert Physiotherapy at Home
Certified physiotherapists visit you at home to provide focused, one-on-one care tailored to your needs. With no travel or waiting rooms, recovery happens in a setting that is comfortable, familiar, and built around your convenience.
Personalised Recovery Programmes
Every treatment plan is designed to suit your condition, goals, and pace. Our physiotherapists follow structured, evolving protocols to ensure consistent progress, with each session aligned to deliver meaningful results.
Trusted Physiotherapists. Real Results.
Our team comprises experienced, background-verified physiotherapists trusted by thousands of families. With a strong focus on safety, reliability, and clinical outcomes, we make recovery at home both effective and reassuring
Patient Testimonials
Portea Physiotherapists for Home Visits
Meet some of our experienced and dedicated healthcare professionals

Dr. Lokesh G
Physiotherapist
Specializations
Experienced in Neurological rehabilitation, Orthopaedic physiotherapy, and Paediatric care
Delivers structured, high-impact treatment plans across neuro, ortho, and paediatrics—ensuring safety, comfort, and measurable recovery at every stage.

Dr. Mohammed Sarwar
Physiotherapist
Specializations
Experienced in Neurological rehabilitation, Adult physiotherapy, and Paediatric care
Combines deep clinical expertise with a compassionate approach, supporting both adults and children through neuro and physical rehabilitation that promotes long-term independence and recovery.

Dr. Nelapati Divya
Physiotherapist
Specializations
Skilled in Orthopaedic rehabilitation, Manual therapy techniques, and Paediatric physiotherapy
Brings a personalised, hands-on approach to healing—combining structural expertise with paediatric sensitivity to restore movement, relieve pain, and improve everyday function.

Dr. Naveen V
Physiotherapist
Specializations
Trained in Pain management, Cardiac and Orthopaedic rehabilitation, Neurological care, and Neural tissue mobilisation
Brings clinical precision and empathy together—designing science-backed recovery protocols for pain relief, nerve mobilisation, and cardio-neuro-ortho rehabilitation across all age groups

Dr. Miloni Savla
Physiotherapist
Specializations
Holds an MPT in Orthopaedics with a focus on Musculoskeletal rehabilitation and strength recovery
Delivers focused, movement-oriented therapy grounded in orthopaedic science—helping patients rebuild strength, restore function, and return to daily life with confidence
Other Cities
Physiotherapy Treatments

acl injuries
The ACL (anterior cruciate ligament) is one of the most important ligaments of the knee, giving it stability. The ACL achieves this role by preventing excessive twisting , straightening of the knee (hyperextension) and forward movement of the tibia on the femur. When these movements are excessive and beyond what the ACL can with stand, tearing to the ACL occurs .This condition is known as an ACL tear and may range from a small partial tear resulting in minimal pain ,to a complete rupture of the ACL resulting in significant pain and disability, requiring comprehensive rehabilitation and potentially surgery.
grades of acl injury
Grade 1:- A small number of fibers are torn resulting in some pain but the joint will function relatively normally.
Grade 2:- A large number of fibers are torn and the knee joint will lose a lot of functionality.
Grade 3:- The ACL ligament is completely torn and the knee becomes unstable . there will be very little if no function of the knee. In this grade most likely surgery is required.
These Might be of Interest
causes of acl tear
An ACL (anterior cruciate ligament) tear is a common but serious knee injury, particularly prevalent in certain sports and activities. The primary causes include:
- Violent Over-Twisting of the Knee: This can occur during activities that involve sharp turns or sudden movements, leading to overstretching or tearing of the ligament.
- Sudden Changes in Direction: Rapid shifts in movement, especially during high-speed activities, can put extreme stress on the ACL.
- Prevalence in Skiing: Skiing often involves both a combination of quick directional changes and potential for awkward falls, making it a common cause of ACL injuries.
- Hyperextension: Overextending the knee joint or applying excessive force to the back of the lower leg can strain or tear the ACL.
- Contact Sports: Sports like football, rugby, and basketball, which involve physical contact and rapid directional changes, frequently see ACL injuries.
- Demanding Physical Activities: Any sport or activity requiring sudden stops, jumps, or rapid changes in direction can increase the risk of an ACL tear.
Understanding these causes is crucial for athletes and individuals engaged in these activities to take preventive measures and minimize the risk of ACL injuries.
symptoms of acl tear
An ACL (anterior cruciate ligament) tear is a significant injury to the knee, manifesting through several distinct symptoms:
- Audible Pop Sound: Often, at the moment of injury, a loud pop or snap can be heard, signaling the tearing of the ligament.
- Pain Levels: For minor tears, pain may start off as mild but gradually intensifies. The discomfort is usually more pronounced during movement or when putting pressure on the knee.
- Swelling and Stiffness: The knee typically swells within a few hours of the injury, leading to stiffness and reduced range of motion.
- Unnatural Knee Movement: The knee may exhibit abnormal movements or feel like it’s giving way, especially in cases of a complete tear.
- Weight-bearing Difficulties: In severe cases, such as a major tear, the leg may become unable to support weight, making standing or walking difficult and painful.
These symptoms can vary in intensity and may be accompanied by a feeling of instability in the knee. Immediate medical attention is recommended to assess the extent of the injury and to plan appropriate treatment.
the major goals of rehabilitation of the acl injured
Rehabilitation following an ACL (anterior cruciate ligament) injury is a critical process, aimed at achieving several major goals for a full and sustainable recovery:
- Gaining Functional Stability: The first and foremost goal is to restore stability to the knee. This involves exercises that strengthen the muscles around the knee joint, ensuring they can effectively support and stabilize the knee during various activities.
- Repairing Muscle Strength: Recovery focuses on rebuilding the strength of muscles affected by the injury, particularly the quadriceps and hamstrings. Strengthening these muscle groups is essential for supporting the knee and facilitating normal movement.
- Reaching Optimal Functional Level: The rehabilitation process aims to help patients regain the highest possible level of functionality. This encompasses daily life activities as well as specific sports or professional tasks, tailored to the individual’s lifestyle and goals.
- Decreasing Re-Injury Risk: A crucial part of rehab is implementing strategies to minimize the likelihood of future injuries. This includes educating patients on proper movement techniques, safe participation in sports, and exercises to maintain knee health and prevent re-injury.
These objectives are pursued through a personalized rehabilitation program, often under the guidance of physiotherapy professionals, to ensure a safe and effective return to pre-injury levels of activity.
physical therapy for acl tear
Before any treatment , encourage strengthening of the quadriceps and hamstrings, as well as ROM exercises. Performance of ROM helps reduce the amount of effusion and help the patient regain motion and strength.
acute phase
price –should be used in order to reduce swelling and pain , to attempt full range of motion and to decrease joint effusion.
Exercises for ACL tear rehabilitation should focus on:
- Range of Motion (ROM): Gradually increasing knee flexibility through safe, guided movements.
- Strengthening Quadriceps and Hamstrings: Building muscle strength around the knee to support and stabilize the joint.
- Proprioception Training: Enhancing the knee’s awareness of position and movement, crucial for preventing re-injury and improving balance.
These exercises aid in effective recovery and long-term knee health.
Rehabilitation protocol in acute phase
the rehabilitation protocol for an acl tear in the acute phase is comprehensive, focusing on various aspects of recovery to ensure effective healing:
- Static Quads/SLR (Straight Leg Raises): These exercises aim to strengthen the quadriceps without straining the knee joint, crucial for early-stage recovery.
- Ankle DF/PF (Dorsiflexion/Plantarflexion) for Circulation: Enhancing ankle movement helps improve blood circulation, reducing swelling and promoting healing.
- Knee Flexion/Extension in Sitting: Gently bending and straightening the knee in a controlled manner helps regain range of motion.
- Patellar Mobilisations: These are techniques used to maintain the mobility of the kneecap, which is vital for knee function.
- Gluteal Medius Work in Side Lying: Strengthening the gluteal muscles, especially the medius, is important for hip stability and overall lower limb alignment.
- Glute Exercises in Prone: Performing glute strengthening exercises in a prone position helps in overall hip and knee stability.
- Knee Flexion in Prone: This helps in increasing the knee’s bending ability in a safe, controlled manner.
- Weight Transfers in Standing: Practicing shifting weight forwards, backwards, and side-to-side enhances balance and stability.
- Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation (NMES): When combined with exercise, NMES is effective in improving quadriceps strength more than exercise alone. It uses electrical impulses to stimulate muscle contraction, aiding in muscle strengthening and recovery.
This protocol aims at a holistic approach to ACL tear rehabilitation, addressing muscle strength, joint mobility, balance, and overall functional improvement during the crucial early phase of recovery.
post operative treatment
Closed chain exercises are used to emphasize early and long term maintenance of full extension.
The therapy protocol may be divided into 4 phases
Phase 1
This is the preoperative period when the goal is to maintain full ROM
Phase 2 (0-2 week)
The goal is to achieve full extension , maintain quadriceps control, minimize swelling, and achieve flexion to 90 degree.
Phase 3 (3-5 week)
Maintain full extension and increase flexion up to full ROM . stair climbers and bicycle may be used.
Phase 4 (6 week)
Increase strength and agility, progressive return to sports .Return to all sports without activity may take 6-9 months and should be closely monitored by the surgeon and physical therapist
Other treatment – (injection , manipulation)
knee brace
The use of knee braces remains a highly controversial topic, braces are well accepted by the patient ,but most biomechanical studies do not support their use. Studies have shown that functional bracing can limit anterior translation of the tibia at low loads. Most braces have been found to decrease the reaction time of the hamstring muscles.
open chain exercises
This is a maintenance phase .The patient’s timeframe for returning to sports depends on his/her strength, ROM ,and the type of fixation that was performed.
how we can help on acl tear?
At Portea, we specialize in providing comprehensive at-home healthcare services, including expert physiotherapy for acl injury. Choosing Portea means the clinic comes to you, alleviating the stress and inconvenience of traveling. Simply call us, and our experienced medical professionals, adept in ACL injury management and rehabilitation, will be at your doorstep promptly. Whether you require treatment for an ACL tear, physiotherapy for acl tear, or post-operative care, Portea is just a call away, ready to cater to all your healthcare needs with efficiency and empathy.
With Portea, you’re not just getting a service ; you’re gaining a partner in your journey to recovery and well-being. We also offer a range of superior healthcare services, including doctor consultations, medical equipment, nursing home care, and dedicated caretakers. Rely on us for top-tier healthcare solutions tailored to your requirements.
meet our renowned physiotherapists
Our renowned physiotherapists for ACL tear are:
Dr Pinki:
Dr. Pinki is a M.P.T in Ortho with 3+ years of experience. She is currently working at Portea Medical.
faqs
Can you still walk with a torn ACL?
Yes, it’s possible to walk with a torn ACL, but it depends on the severity of the tear and individual pain tolerance. Walking may be challenging and could exacerbate the injury. Caution and minimal weight-bearing are advised, and using a brace or crutches may be necessary for support and stability.
What exercise is best for ACL injuries?
For ACL injuries, low-impact exercises are most beneficial:
- Stationary Biking: Helps maintain cardio fitness without stressing the knee.
- Swimming: Provides resistance training and aerobic exercise, ideal for knee support without impact.
- Leg Raises: Strengthens quadriceps without putting pressure on the knee.
- Hamstring Curls: Enhances strength and stability in the back of the thigh.
- Balance Exercises: Such as standing on one leg, to improve stability and proprioception.
Consult a healthcare professional for a personalized exercise plan, especially in the early stages of recovery.
Is ACL a major injury?
Yes, an ACL (anterior cruciate ligament) injury is considered a major injury. It can lead to knee instability, limit physical activity, and often requires a lengthy recovery process. Treatment may involve extensive physiotherapy and, in severe cases, surgery. Early and proper management is crucial for optimal recovery.
Which food is recommended for ACL tear?
For an ACL tear, a diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods is recommended. This includes omega-3 fatty acids from fish like salmon and mackerel, nuts, and seeds. Incorporate plenty of fruits and vegetables, particularly leafy greens and berries, for their antioxidants. Protein-rich foods aid in tissue repair, while calcium and vitamin D are important for bone health. Spices such as turmeric and ginger can also help reduce inflammation.
What to avoid with a ACL tear?
With an ACL tear, it’s important to avoid:
- High-Impact Activities: Sports and exercises that involve jumping, running, or sudden changes in direction can worsen the injury.
- Weight-Bearing Exercises: Initially, avoid putting too much weight or strain on the injured knee.
- Rapid Movements: Quick twists or turns can increase the risk of further damage to the ACL.
- Overstretching: Be cautious not to overstretch or stress the injured knee during physical activity or exercises.
- Neglecting Rehabilitation: Skipping prescribed rehabilitation exercises or physical therapy sessions can slow down or impede the healing process.
Doctor Consultation
Nursing
Physiotherapy
Trained Attendant
Elder Care
Mother & Baby Care
Lab Tests
Medical Equipment
Speciality Pharma
Critical Care